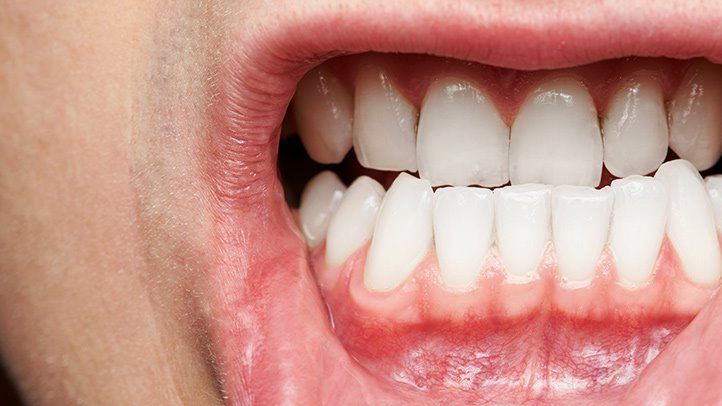
Factors That Can Increase Your Vulnerability to Gum Disease
Gum disease occurs due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque on your teeth and gums, leading to inflammation and, eventually, the breakdown of your gums and bone. Symptoms of Monterey gum disease include red, swollen, bleeding gums, bad breath, and tooth sensitivity. If left untreated, it can result in tooth loss and even contribute to other health problems such as heart disease and diabetes. The following are the risk factors of gum disease:
Poor oral health care habits
Neglecting daily oral hygiene practices such as brushing and flossing can allow bacteria to accumulate in your mouth and form plaque on the teeth and gums. Plaque buildup can lead to inflammation of your gums, an early stage of gum disease known as gingivitis. If not treated promptly, gingivitis can advance to periodontitis, resulting in irreversible damage to your teeth and supporting structures.
Genetics
Research suggests that people with a family history of gum disease are at a higher risk of developing the condition, even if they practice good oral hygiene. This increased risk is due to the inheritance of certain genetic traits that can affect your body’s immune response to bacterial infections in your mouth. Certain genetic variants can also exacerbate the progression of gum disease. Studies have identified specific gene variants that can affect the production of enzymes and proteins involved in the immune response and tissue repair in the gums. These variants can lead to an overactive immune response, causing inflammation and damage to your gums and impairing healing.
Hormonal changes
A fluctuation in hormone levels during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can increase gum disease susceptibility. These hormonal changes can cause the blood vessels in your gums to become more permeable, allowing harmful bacteria to enter and thrive, leading to inflammation and infection. Additionally, they can affect your body’s ability to fight off infections, making it harder to combat gum disease.
Smoking
When you smoke, the chemicals in tobacco products can damage your gums and teeth. This unhealthy habit can reduce blood flow to your gums, making it harder for them to heal and fight off infections. It can also weaken your immune system, making it easier for harmful bacteria to take hold of your mouth. Smoking can also mask the symptoms of gum disease, making it harder to diagnose and treat. You may experience less bleeding and swelling of your gums than non-smokers, even when you have gum disease, which can give you a false sense of security, leading you to delay seeking treatment.
Poor nutrition
When you do not consume a balanced diet with adequate nutrients, your immune system may become compromised, making you more susceptible to gum disease. Poor nutrition can also affect the integrity of your oral tissues, increasing your vulnerability to harmful bacteria. Furthermore, a diet lacking key nutrients such as vitamin C, vitamin D, and calcium can weaken your bones and teeth, exacerbating gum disease progression. Vitamin C is essential for developing healthy gum tissue, while vitamin D and calcium are vital for strong bones and teeth.
Call the Perio & Implant Center or book an appointment online to learn more about gum disease.